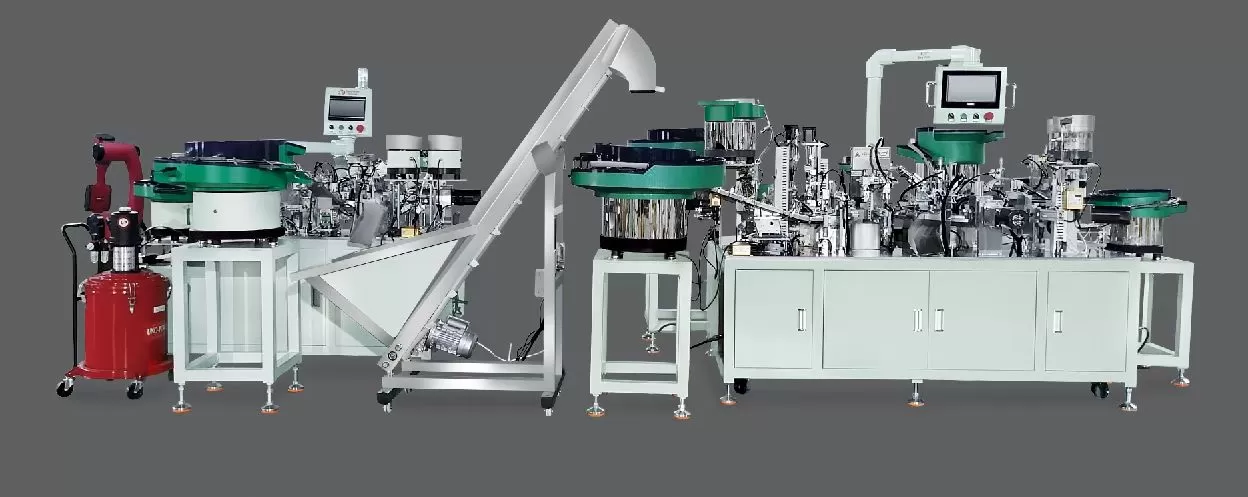
The Illustrated Operation Flowchart of a Jieyang Hinge Automatic Assembly Machine serves as a critical visual guide for manufacturers, outlining the step-by-step process of automating hinge production. In an era where efficiency and precision are paramount, such a flowchart demystifies complex assembly sequences, enabling operators and engineers to align production workflows with optimal performance. For companies like Sanyhore—specialized in designing and manufacturing hinge assembly machines, telescopic drawer slide assembly machines, and roll forming machines—this flowchart is not just a technical diagram but a foundation for delivering reliable, high-speed solutions tailored to diverse production needs.
1. Design and Initial Planning Phase
The first stage of the flowchart begins with design and initial planning, a phase where customer requirements, production volume, and hinge specifications are meticulously analyzed. Engineers use 3D modeling software to simulate the entire assembly process, identifying potential bottlenecks and optimizing component layout. This step ensures that the machine is engineered to handle specific hinge types—whether small precision hinges for electronics or larger industrial hinges—while adhering to tight dimensional tolerances. By integrating modular design principles, the machine can be adjusted to accommodate minor variations in hinge dimensions, reducing setup time and minimizing waste.
2. Component Feeding and Orientation System
Next, the flowchart transitions to the component feeding and orientation system, a critical link in maintaining continuous production flow. The system typically includes vibratory bowls, linear feeders, and orientation chutes, which handle raw materials such as metal blanks, pins, springs, and covers. Vibratory bowls use controlled vibration to lift and orient components, ensuring they move in a consistent direction toward the assembly area. Linear feeders then guide the components along precision tracks, with orientation chutes correcting any misalignment to prevent jams. This stage is designed to handle a high throughput of components, often exceeding 100 hinges per minute, depending on the machine’s capacity.
3. Precision Positioning and Gripping Mechanism
Accurate positioning is the backbone of the assembly process, and the flowchart highlights the role of the precision positioning and gripping mechanism. Equipped with advanced sensors and vision systems, the machine’s robotic grippers or mechanical arms locate each component with sub-millimeter precision. CCD cameras scan components to verify orientation and presence, while coordinate systems (e.g., X-Y-Z stages) adjust the position of parts before assembly. Grippers, often with soft jaws or vacuum cups, securely hold components to prevent damage, ensuring they remain stable during the next assembly step. This stage minimizes human intervention, reducing errors and enhancing production consistency.
4. Assembly and Press-Fitting Process
The core assembly and press-fitting process follows, where individual components are joined to form the final hinge. Depending on hinge type, this may involve processes like riveting, welding, or snap-fitting. For example, a typical hinge assembly might require aligning the leaf, pin, and spring, then inserting the pin through pre-drilled holes using a precision press. The press applies controlled force to ensure the pin is fully seated without deforming the material, with pressure sensors monitoring the process to maintain quality. During this stage, the flowchart also includes checks for component engagement—ensuring the leaf and pin rotate smoothly, a key functional requirement for the hinge.
5. Quality Inspection and Defect Rejection
Post-assembly, the flowchart emphasizes the quality inspection and defect rejection stage, a critical step to ensure only合格产品 leave the production line. The inspection system integrates visual inspection cameras, dimension measurement tools (e.g., laser scanners), and force testers to verify key parameters: surface finish, dimensional accuracy, pin insertion depth, and rotational resistance. Defective hinges—such as misaligned components, uneven gaps, or weak joints—are automatically diverted to a reject chute, while non-defective units proceed to the next stage. This real-time quality control prevents downstream issues and ensures compliance with customer standards.
6. Finished Product Conveying and Packaging
The final stage of the flowchart involves conveying and packaging the finished hinges. Automated conveyor belts, often with infeed/outfeed buffers, transport the合格产品 to packaging stations. Here, the hinges are either placed into individual blister packs, cartons, or bulk containers, depending on customer requirements. The packaging process may include labeling with batch numbers or production dates, ensuring traceability. This integration of conveying and packaging minimizes manual handling, reducing labor costs and accelerating the overall production cycle.
7. Integrated System Monitoring and Control
Throughout the process, the flowchart underscores the importance of integrated system monitoring and control, managed by a central PLC (Programmable Logic Controller). Sensors throughout the machine—including temperature, pressure, and speed sensors—transmit real-time data to the PLC, which adjusts parameters to maintain optimal performance. Alarms are triggered for anomalies like component jams or tool wear, allowing operators to intervene promptly. This level of control not only ensures consistent production but also extends machine lifespan by preventing premature wear and tear.
Common Questions About Hinge Automatic Assembly Machines
Q: How does the flowchart help in troubleshooting production issues?
A: The flowchart provides a visual breakdown of each step, allowing operators to identify where a problem might occur—e.g., a jam in the feeding system or misalignment in the assembly stage—enabling targeted diagnostics.
Q: Can the machine be adapted for different hinge models?
A: Yes, with modular design, the system can be reconfigured to accommodate varying hinge sizes and types, reducing changeover time from hours to minutes.
Q: What is the typical production capacity of a Jieyang hinge automatic assembly machine?
A: Capacities range from 60 to 200 hinges per minute, depending on hinge complexity and machine configuration, with Sanyhore offering customized solutions to match specific production demands.
For manufacturers seeking to enhance hinge production efficiency, Sanyhore’s expertise in designing and manufacturing hinge assembly machines, telescopic drawer slide assembly machines, and roll forming machines is unmatched. With a focus on precision, reliability, and customization, we help businesses reduce costs and improve output. Contact our sales manager today for a detailed consultation: +86 13425506550 or email info@sanyhore.com.