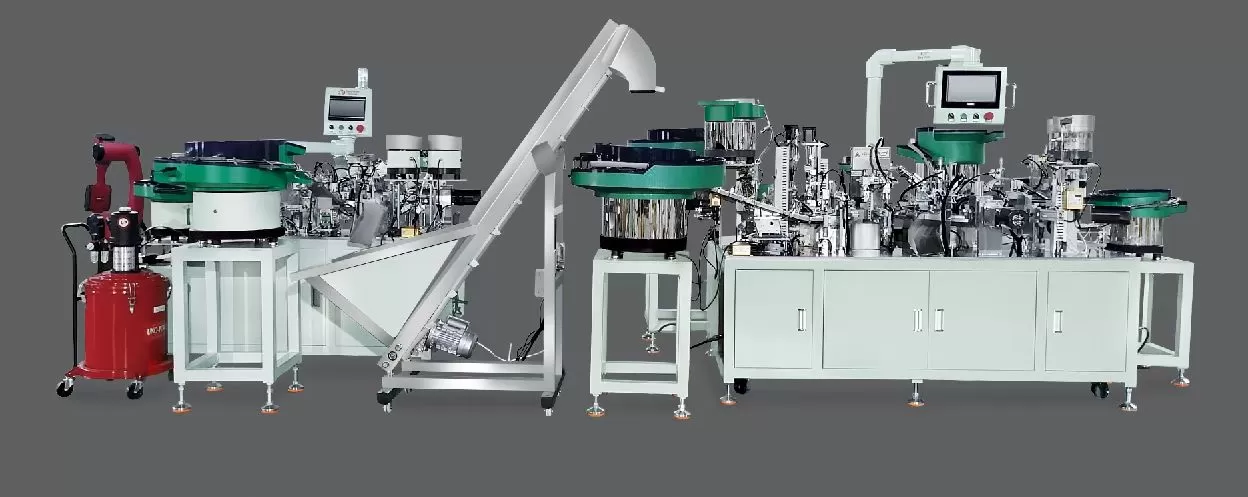
- 副本.png)
The parameter adjustment process is critical for ensuring the optimal performance of Jieyang hinge automatic assembly machines. As a core part of hinge production lines, these machines rely on precise parameter settings to maintain consistent joint quality, minimize downtime, and boost overall productivity. This guide outlines essential steps, key parameters, and best practices to master the adjustment process effectively.
Initial Setup Requirements
Before starting adjustments, ensure the machine is in a stable pre-operational state. First, inspect for loose connections, worn parts, or debris in critical areas like guide rails and tooling. Verify power supply stability and check if the air pressure (for pneumatic systems) or hydraulic oil levels are within specified ranges. Equally important, reference the machine’s technical manual to identify parameters specific to the hinge model being processed—different hinge types (e.g., butt hinges, continuous hinges) may require unique adjustment criteria to ensure compatibility with the assembly mechanism.
Key Parameters for Calibration
Several core parameters directly impact assembly outcomes. Pressure settings, for instance, control the force applied during pin insertion or component joining. Insufficient pressure may result in loose joints, while excessive pressure can damage delicate materials (e.g., brass or stainless steel hinges). Positioning accuracy, adjusted via servo motors or linear guides, ensures components align perfectly—misalignment here often causes skewed hinges or jammed parts.
Speed parameters, including cycle time and feeding rate, must be balanced to avoid bottlenecks. Too fast, and components may not seat properly; too slow, and production efficiency drops. Additionally, sensor sensitivity settings (e.g., for detecting component presence/absence) are critical—poor sensitivity can lead to missed parts or false alarms, disrupting the production flow.
Step-by-Step Adjustment Protocol
To begin, power on the machine and access the HMI (Human-Machine Interface). Input the specific hinge model to load the pre-configured parameter template, reducing manual input errors. Start with pressure adjustments: set a moderate initial value, run a short production trial, and inspect joints for tightness and deformation. Use calipers to check dimensions, and tweak the pressure in small increments (e.g., 0.1 MPa steps) until the joint meets quality standards.
For positioning accuracy, use the machine’s built-in alignment tools to verify component placement. Adjust the X, Y, and Z axes via the HMI, testing with sample parts and measuring with precision tools. If discrepancies occur, recalibrate the guide rails or servo motor encoders as specified in the manual.
Next, optimize speed parameters. Gradually increase the cycle time from the minimum setting, monitoring for jams or component misalignment. Stop and adjust if defects appear, then re-test. For sensor calibration, simulate component absence/presence scenarios to ensure the machine pauses or triggers alerts correctly—this prevents errors and reduces material waste.
Troubleshooting Common Adjustment Issues
Even with careful setup, operators may face adjustment challenges. A frequent problem is unstable pressure, often caused by air pressure fluctuations or worn hydraulic components. In such cases, check the air compressor and pressure regulators, replacing worn parts (e.g., valves or cylinders) to restore stability.
If positioning errors persist, verify the alignment of guide rails and servo motor encoders. Misalignment here can lead to inconsistent spacing, so use the machine’s alignment laser tools to adjust and recheck with calipers. For sensor failures, inspect the sensing elements for dirt or damage—cleaning with compressed air or replacing damaged sensors often resolves sensitivity issues.
Benefits of Proper Parameter Adjustment
Implementing a systematic adjustment process delivers tangible benefits. By optimizing pressure, speed, and positioning, production efficiency can increase by 15–20%, reducing cycle time and lowering labor costs. Consistent parameters also minimize product defects, improving quality and customer satisfaction. Additionally, well-adjusted machines experience less mechanical stress, extending service life and reducing maintenance expenses.
For hinge manufacturers seeking reliable, high-performance automatic assembly machines, Sanyhore is your trusted partner. As a professional producer of hinge assembly machines, telescopic drawer slide assembly machines, and roll forming machines, we offer comprehensive support—including parameter adjustment training and on-site technical guidance—to ensure your production runs smoothly. Our machines are engineered for stability and efficiency, meeting diverse manufacturing needs. Contact Sanyhore today to optimize your hinge production line: +86 13425506550 or email info@sanyhore.com for personalized solutions.
Common SEO Questions for Hinge Assembly Machine Users
Q1: How often should I adjust parameters on my automatic hinge assembly machine?
A1: Regular adjustments are recommended after changing hinge models, weekly for high-volume production, and immediately if defects or jams occur.
Q2: Can I adjust parameters without professional training?
A2: Basic adjustments (e.g., pressure and speed) can be done by trained operators, but complex tuning (e.g., sensor calibration) is best handled by Sanyhore’s technical team. Contact us for support.
Q3: What tools do I need for parameter adjustment?
A3: Essential tools include calipers for dimension checks, pressure gauges, and the machine’s HMI system. Sanyhore provides toolkits with our machines for convenience.
Q4: How does parameter adjustment reduce production costs?
A4: Proper adjustment minimizes material waste, lowers machine downtime, and extends equipment life, leading to a 15–25% decrease in overall production costs.
Q5: Does Sanyhore offer parameter adjustment training?
A5: Yes, we provide on-site and online training sessions to ensure your team can perform adjustments efficiently and independently.