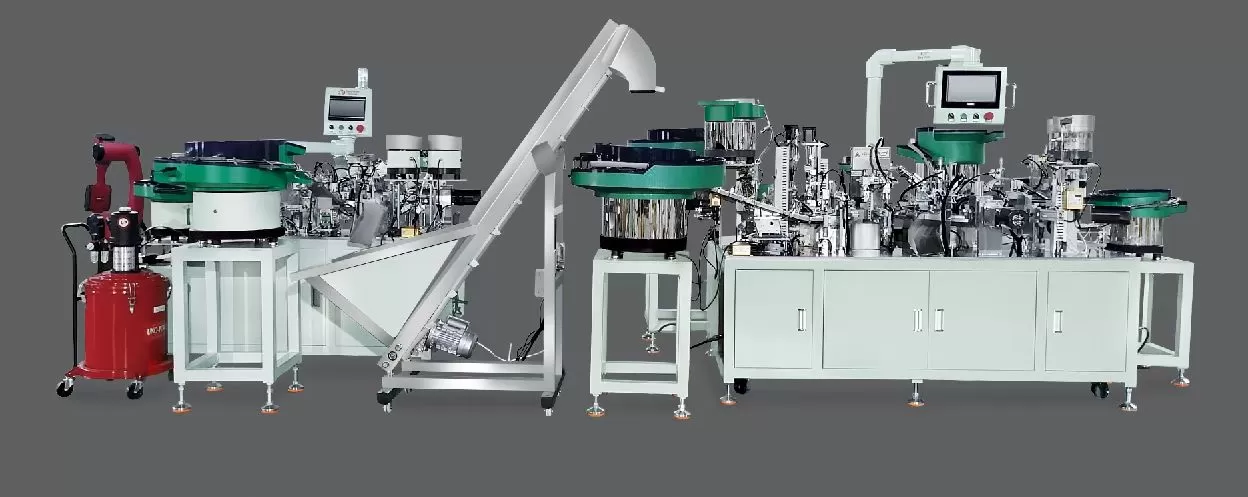
The transition from manual to automated hinge assembly has been a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, driven by the need for higher efficiency, consistent quality, and reduced labor costs. At the heart of this evolution lies a blend of mechanical engineering, materials science, and control systems—collectively known as the "science of automatic hinge assembly." This field leverages precise engineering to streamline the complex process of joining hinge components, ensuring each unit meets rigorous standards while scaling production capabilities. Understanding this science not only highlights the technical advancements in manufacturing but also reveals how modern systems like Sanyhore’s hinge assembly machines integrate seamlessly into industrial workflows.
Understanding the Mechanics of Hinge Assembly
A hinge, in its simplest form, consists of two or more rigid components (e.g., leaves, pins, bushings) joined by a rotating joint. The assembly process demands meticulous alignment, as misalignment can lead to premature wear, noise, or failure. Traditional manual assembly relies on human dexterity, which is limited by speed, consistency, and fatigue. Automatic systems address these challenges by mimicking human precision through mechanical and electronic means. Key mechanical principles include:
- Kinematic Pairing: Ensuring the hinge’s rotating joint has minimal friction while maintaining structural integrity, often achieved through precise tolerances (as low as 0.01mm) in component dimensions.
- Force Distribution: Controlling the pressure applied during pin insertion or welding to prevent damage to delicate materials like brass or stainless steel, critical for durability in applications such as furniture or automotive parts.
Core Components of Automatic Hinge Systems
An automatic hinge assembly machine is a symphony of mechanical, electrical, and software components working in harmony. Central to its functionality are:
- Feeding Systems: Vibratory bowls or linear feeders that orient and deliver hinge components (e.g., leaves, pins) to the assembly station. These systems use vibration and track design to ensure components are correctly positioned before processing.
- Robotic Manipulators: Servo-driven arms with end-effectors (e.g., grippers with vacuum cups) that pick, place, and align parts with sub-millimeter accuracy. Advanced robots can handle multiple tasks, such as inserting pins and pressing bushings, in a single cycle.
- Control Systems: Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) and motion controllers that coordinate all components. These systems use preprogrammed sequences to execute tasks, with feedback loops adjusting for variables like component size or material thickness.
Precision Engineering in Hinge Assembly
Precision is the backbone of automatic hinge assembly, as even minor deviations can compromise performance. Modern machines achieve this through:
- Laser Alignment: Non-contact laser sensors measure component positions in real time, adjusting robotic movements to maintain alignment within acceptable limits.
- Material Compatibility: The science of materials ensures components like stainless steel pins or polymer bushings are joined using methods (e.g., press fitting, ultrasonic welding) that avoid material damage. For example, ultrasonic welding bonds metal surfaces without heat-affected zones, ideal for thin-gauge materials.
- Tolerance Stack-Up Analysis: Engineers use computer-aided design (CAD) to model how individual component tolerances combine, ensuring the final hinge meets functional requirements (e.g., 360° rotation without binding).
Sensors and Feedback Loops in Automation
To maintain consistency, automatic hinge assembly systems rely on closed-loop control, where sensors provide real-time data to adjust processes dynamically. Common sensor types include:
- Vision Sensors: These capture images of components to verify part orientation, detect defects (e.g., bent leaves), or measure dimensions. Machine vision systems can process thousands of parts per minute, far exceeding human inspection speed.
- Force Sensors: Integrated into grippers or press tools, these sensors monitor the force applied during insertion or joining. If excessive force is detected, the system automatically reduces pressure to prevent damage, ensuring each hinge meets torque or load specifications.
- Proximity Sensors: These detect the presence/absence of components, preventing jams and ensuring the assembly sequence proceeds only when parts are correctly positioned.
Quality Control in Automated Processes
Automation transforms quality control from a post-production check to an integrated part of the manufacturing cycle. Key techniques include:
- In-Process Measurement: Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMMs) or optical comparators scan hinge dimensions online, with data logged to a database for trend analysis.
- Statistical Process Control (SPC): By tracking key metrics (e.g., pin alignment, torque values) over time, manufacturers can identify anomalies early, reducing scrap rates and rework.
- 100% Testing: Unlike manual inspection, automated systems test every hinge, ensuring no defective units leave the production line. For example, a hinge might undergo a 10,000-cycle durability test to verify rotational performance.
Future Trends in Hinge Assembly Technology
The science of automatic hinge assembly continues to evolve, driven by Industry 4.0 demands for smarter, more flexible manufacturing:
- AI-Driven Optimization: Machine learning algorithms analyze production data to predict tool wear, adjust process parameters, and minimize downtime.
- Modular Design: Systems that can be reconfigured quickly to produce different hinge types, reducing setup time and enabling small-batch production.
- Sustainability Integration: Machines that use energy-efficient motors, recycled materials, and reduced waste, aligning with global sustainability goals.
For manufacturers seeking to adopt automatic hinge assembly technology, Sanyhore stands out as a trusted partner. As a professional producer of hinge assembly machines, telescopic drawer slide assembly machines, and roll forming machines, we combine decades of engineering expertise with cutting-edge innovation to deliver solutions tailored to your production needs. Whether you require high-speed production lines or flexible systems for custom hinges, our machines integrate seamlessly into existing workflows, boosting efficiency and quality.
To explore how automatic hinge assembly can elevate your manufacturing process, contact our team today at +86 13425506550 or via email at info@sanyhore.com. Let’s build the future of hinge production together.